According to statistics, the global indoor positioning market in 2023 is estimated at $8.8 billion. It’s projected that by 2027 its volumes will reach $27 billion, so many companies are striving to introduce indoor positioning into their infrastructure. So, the question arises - which technology is the better option? In this article, we'll take a look at the two most common solutions - UWB vs. Bluetooth® LE, and compare their features and advantages.
What is Bluetooth® LE?
Bluetooth® Low Energy is a wireless communication protocol designed specifically for low energy consumption. It’s an effective alternative to classic Bluetooth® and offers almost the same features but with lower energy consumption. Due to this, the technology is often used in systems where battery life plays an important role.
When implementing Bluetooth® LE, special sensors (known as beacons) are used, which are placed in different parts of the building. With a certain frequency, they send out signals that are received by a smartphone with a pre-installed mobile application. Depending on the tasks and positioning, various information can be delivered to visitors, such as location information, ads, push notifications, etc.
Bluetooth® LE is a radio wave technology based on the FHSS method. During the operation of the sensors, there is an abrupt change in the frequency of radio signals (up to 1600 per second) with a random sequence, which is determined only by the transmitter.
The technology is used to transmit data over low bandwidth channels. The maximum transfer rate is 2 Mbps, and the range depends largely on the environment. It averages between 10 and 30 m but can be as high as 100 m. The power consumption of beacons is affected by characteristics such as device implementation and protocol parameters. Typically, during data transmission, it does not exceed 15 mA.
Affordable implementation costs and high location accuracy make Bluetooth® Low Energy a popular solution in many industries. Business owners highly appreciate the technology due to its benefits, such as:
- configuring the infrastructure based on inexpensive equipment;
- long service life of beacons - about 5 years;
- easy installation, configuration, and subsequent use;
- a wide range of features - from positioning to indoor navigation and tracking;
- positioning in real time;
- simple scaling;
- high data transfer rate.
How does UWB work?
Like Bluetooth® Low Energy, UltraWideband (UWB) is a wireless technology that transmits data over short distances with low power consumption. However, it has a wider range (up to 650 ft), which makes it an effective solution for large facilities, including for monitoring the whole territory.
UWB uses ultra-wideband signals with low power spectral density. Radio signals propagate at frequencies of 3.12 -10.6 GHz and are considered rather weak, so they don’t need to be licensed by the SCRF. Based on the needs of your business, the system makes calculations using different methods - TDoA, AoA, ToF, PDoA, and TWR. The accuracy of positioning can be around 4 inches, but it’s important to consider that this number can only be achieved in lab conditions, while real numbers vary on average from 20 inches to 3 ft.
Ultra Wideband technology is based on using special anchors/locators that are placed on the tracked objects. Most often, the TWR (Two Way Ranging) technique is used, which provides high accuracy and stable calculations. The tags send out signals at regular intervals, which are received by several synchronized anchors and transmitted to the servers. Positioning is performed by determining the time it took the radio signals to travel from the sensor to the server.
UWB is usually used in manufacturing - to visualize assets and control the operation of equipment and staff. If needed, the tags are placed in special bracelets that can be used to monitor staff or patients in medical facilities.
The main advantages of Ultra Wideband technology include:
- high-precision location determination;
- high speed of information transfer;
- simultaneously supporting a large number of channels;
- resistance to interference;
- transferring large amounts of data;
- high spectral flexibility;
- wide scaling range in terms of speed.
Technology comparison
When discussing Ultra Wideband vs Bluetooth®, it’s worth noting that both technologies are suitable for determining the location of people or objects. They are based on a local wireless network and are optimal for equipment that requires high positioning accuracy. However, there are many differences between these technologies. For instance, UWB is low-power and transmits data in the range from 3.12 to 10.6 GHz. Bluetooth® LE, on the other hand, uses 2.4 GHz transmission over 80 different channels at 1 MHz each.
Ultra Wideband is more secure, while Bluetooth® Low Energy is more susceptible to attacks or wiretapping. This makes the first option better suited for systems that require a high level of security. Along with this, Bluetooth® LE has a large technological ecosystem that makes it popular in many scenarios. It can be used in almost any area - from retail and shopping malls to healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, and warehouses.
To better understand the UWB/Bluetooth® difference, take a look at their main features in the table below.
| Features | Technologies | |
|---|---|---|
| UWB | Bluetooth® LE | |
| Positioning accuracy | 4-12 in | 3-10 ft |
| Frequency | 3.12 -10.6 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Range | up to 650 ft | up to 330 ft |
| Interference | high resistance to interference | high interference (same frequency as Wi-Fi) |
| Number of beacons/tags in one environment | increased performance due to high unused frequency channels | limited capabilities due to the lower frequency that is applied simultaneously with Wi-Fi channels |
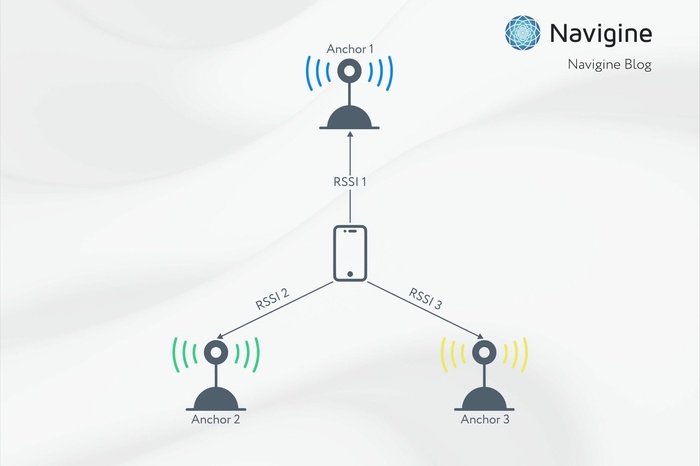
| Positioning algorithms | TWR, TDoA, AoA, ToF | RSSI, AoA |
| Signal absorption | not applicable to ToF, high with RSSI | RSSI distortion, high human absorption |
| Where to use | equipment, staff, vehicles | equipment, staff, vehicles |
| Scalability | possible | possible |
Between the two technologies, it’s worth considering that UWB provides higher accuracy, which makes it suitable for tracking high-value assets. Bluetooth® Low Energy, while less accurate, is more affordable to implement and is widely used for simple positioning solutions that can be easily scaled to meet user needs. Both technologies perform well and can be successfully used for positioning, so the choice between Bluetooth® or Ultra Wideband should be made taking into account the specific needs of your project.
No matter the complexity of your project, Navigine is here to help you choose the most suitable positioning technology option. We work with both UWB and Bluetooth® LE and can provide suitable algorithms and hardware. To learn more about indoor positioning, contact us by filling out the form on our website or by booking a free Zoom demo with our representatives.