For the last few years, location tracking technologies have become extremely popular. Being a topical issue in improving business processes, they are being actively implemented in all spheres of life – from staff monitoring to machinery and equipment tracking. The variety of application spheres leads to emerging new systems and standards ensuring varied localization accuracy in time and space.
Because of the rapid development of navigation devices and equipment, developers often face the problem of choosing the right technology. At the same time, satellite technologies are known to allow detecting the location of objects only in open terrain. However, according to the statistics, only 13% of their time people spend outside or in a car. Thus, for tracking movements in closed spaces or underground, other technologies are necessary – especially if it concerns staff monitoring and ensuring working safety. But is it worth giving preference to new solutions? Are there any compromises? Let’s consider these issues in our article.
Location tracking technologies
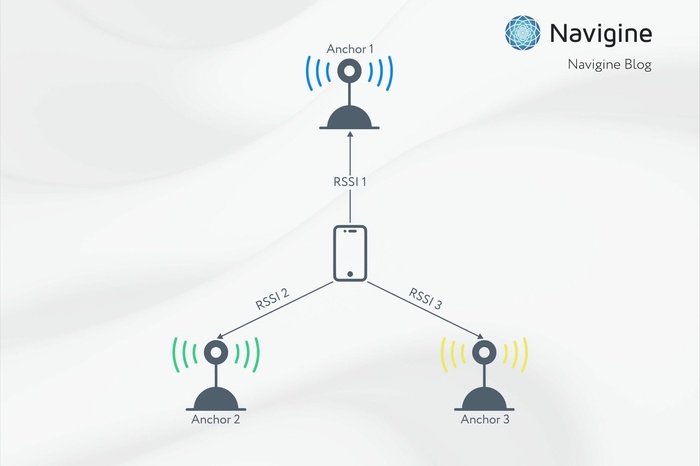
Advanced indoor navigation technologies are based on building movements by distance or fixing different sources of the signal. The most popular ones are Bluetooth, UWB, and Wi-Fi.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless technology of data transmission that ensures quick data exchange between mobile and computer devices. It is used in PCs, smartphones, tablets, headphones, as well as in other systems aimed at positioning with Bluetooth. All these devices can communicate with each other within a radius of up to 10 meters in the old versions of the system and up to 1500 meters starting with Bluetooth 5.0.
The protocol is based on radio waves. The FHSS (Frequency-hopping spread spectrum) method, used in the Bluetooth navigation system, contributes to a jump-like change of signal frequencies (up to 1600 times per second). The sequence of changing signal frequencies is pseudorandom since it can be known to the transmitter which rearranges synchronously between frequencies. Starting with Bluetooth 4.0, the system uses the BLE technology which ensures the connection of gadgets with lower battery consumption.
Bluetooth advantages:
- Simplicity in connecting two devices - you need only a Bluetooth adaptor to establish the connection.
- No necessity for indirect visibility – devices “see” each other while approaching within a particular distance.
- Low energy consumption.
- High speed of data transmission (1 Mb/sec).
Disadvantages:
- Difficulties in detecting a device in the network that has a great number of connections.
- Weak protection, vulnerability to spoofing.
Wi-Fi
At present Wi-Fi is considered one of the most common systems used in Android indoor navigation. It can be found practically in any office, in most private houses and flats. Similar to Bluetooth, this wifi location tracking technology works by measuring a signal and converting it into the distance. However, such a wifi positioning system causes some difficulties as the signal level is insufficient for measuring the exact distance.
Wi-Fi advantages:
- Possibility of deploying a network without a cable.
- Access to the Internet by several users simultaneously within the network range.
- High speed of data transmission.
- Simple settings.
- Safety (the level of exposure from Wi-Fi is much lower in comparison with mobile phones).
Disadvantages:
- Differences in the frequency range in various countries.
- The simplicity of hacking the WEP data encryption standard.
- Low electromagnetic compatibility is connected with the wide use of the 2.4 GHz range by various devices, even by microwaves.
UWB
At present, the UWB indoor navigation of premises is not the most economical but is the most accurate one. The standard uses radio waves that have a short pulse transmission. The distance between UWB devices can be easily defined using measuring the time taken by the radio wave to pass from one device to the other.
The UWB location tracking system development allowed implementing the wireless communication technology that works at short distances. The average speed of data transmission at a distance of 3 meters is on average 480 Mb/sec. UltraBand width signals can keep the structure and consistency even at noise effects since they have low spectral power density.
UWB technology advantages:
- Compatibility with radiofrequency spectrum devices.
- Simultaneous support of a great number of channels.
- High speed of data transmission.
- High level of data protection while transmitting.
- Stable connection at multipath wave propagation.
Disadvantages:
- A small range of signals.
- Creating interference for existing communication lines.
Which technology is the best?
For answering this question, let’s look at the comparative table of the given technologies.
| Parameters | Technology | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| UWB | Wi-Fi | Bluetooth | |
| Accuracy in object localization | 0.5-1m | 1-5m | 1-5m |
| Energy consumption (without charging a smartphone) | 5-6 hours | 1-2 days | 1-2 days |
| Cost | High | Low | Low |
| Spheres of usage | Industry | Industry, healthcare, transport, retail, logistics, property, etc. | Industry, healthcare, transport, retail, logistics, property, etc. |
Taking into account everything mentioned, we conclude that all reviewed systems can be used for solving different tasks. Some systems are suitable for equipment that requires particular accuracy, such as UWB RTLS solutions, while the others are used for saving and reducing energy costs. That’s why all these three technologies are in demand.
Navigine is specialized in implementing the indoor navigation system and offers clients a powerful platform with the iBeacon function of exact localization based on Bluetooth Low Energy. Contact us and we’ll be glad to cooperate with technological companies, mobile application developers, and system integrators who deal with the development and implementation of new navigation technologies.